Introduction to Promises
Promises: A brief introduction
Promise
The Promise object represents the eventual completion (or failure) of an asynchronous operation and its resulting value. A Promise is in one of these states:
- pending: initial state, neither fulfilled nor rejected.
- fulfilled: meaning that the operation was completed successfully.
- rejected: meaning that the operation failed.
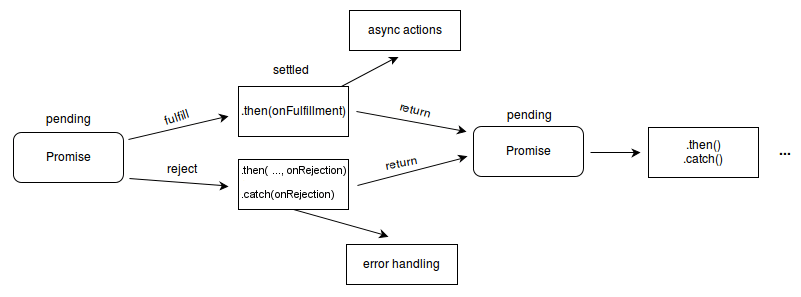 Image by MDN. Used under Creative Commons license.
Image by MDN. Used under Creative Commons license.
A simple, pratical example will be
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
const lateBloomer = (bloomed) => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if (bloomed) {
setTimeout(() => resolve("The flower bloomed."), 300)
} else {
reject(Error("The flower won't bloom!"));
}
})
};
Here we are creating a lateBloomer function that accepts a boolean argument and,
- fullfill the promise after 300 milliseconds “bloomed” value is true.
- reject the promise if “bloomed” value is false.
Conventionally, a promise is called like this
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
lateBloomer(false).then(response => {
// success callback
console.log(response)
},err => {
// error callback
console.log(err.message)
},
);
async / await
Handling promises became much easier with async/await
async: The async function declaration creates a binding of a new async function to a given name. The await keyword is permitted within the function body, enabling asynchronous, promise-based behavior to be written in a cleaner style and avoiding the need to explicitly configure promise chains.
await: The await operator is used to wait for a Promise and get its fulfillment value. It can only be used inside an async function or at the top level of a module.
An example would be,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
const lateBloomerAsAsync = async (bloomed) => {
if (!bloomed) {
throw new Error("The flower won't bloom!");
}
await new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(resolve, 10000));
return 'The flower bloomed.';
};
async function logBloomStatusAsAsync() {
try {
const flowerStatus = await lateBloomerAsAsync(true);
console.log(flowerStatus);
} catch (err) {
console.log(err.message);
}
}
logBloomStatusAsAsync();
Thats’s all for today. Happy coding